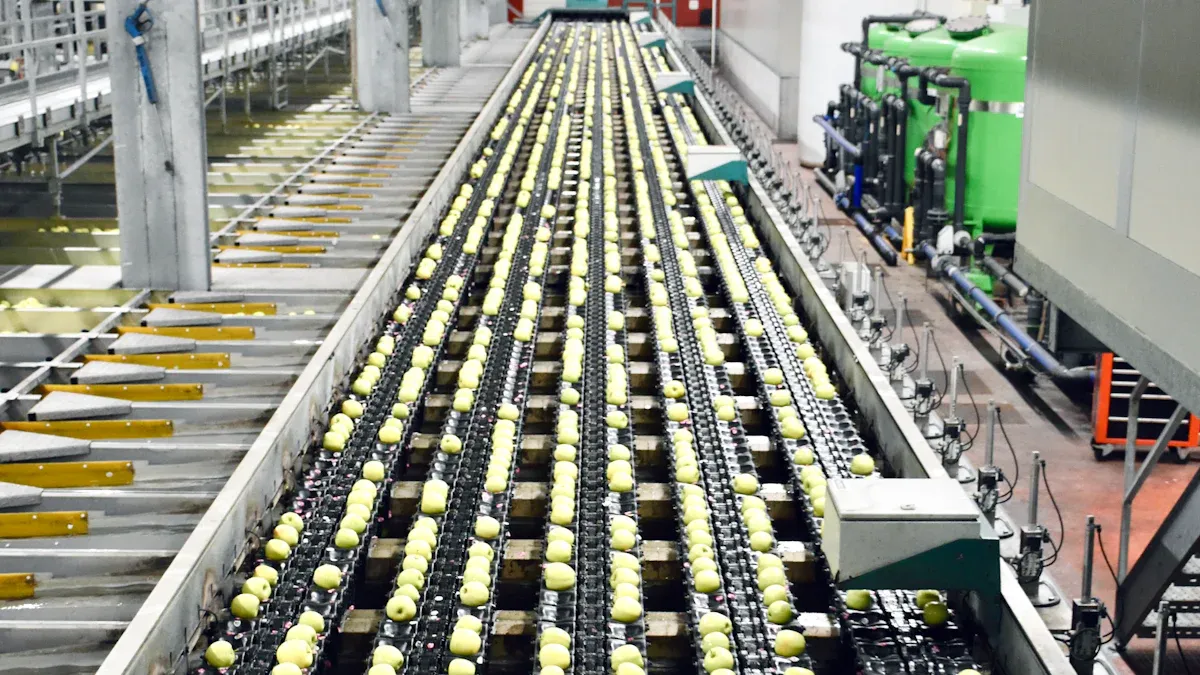
Food factories face growing pressure to reduce waste and pollution from oil used in cooking processes. Oil purifiers provide practical solutions that support sustainability and limit the negative impact of food production on the environment. Cleaner oil means safer food and less waste, helping companies adopt responsible solutions for a healthier future.
Oil Waste Challenges in Food Factories
Sources of Oil Waste
Food factories generate oil waste from several sources. Used cooking oil comes from fryers and other equipment during daily operations. Packaging materials, such as plastic containers and cardboard boxes, also contribute to waste when transporting oil.
Tip: Regular monitoring of oil usage helps factories identify major sources of waste and improve efficiency.
Environmental Impact of Improper Disposal
Improper disposal of used cooking oil can harm the environment. When oil enters landfills or water systems, it increases emissions and pollutes soil and water. Factories that fail to manage oil waste properly raise their emissions and worsen the impact on the environment.
A table below shows common consequences of poor oil disposal:
| Disposal Method | Environmental Effect | Emissions Level |
|---|---|---|
| Landfill | Soil contamination | High |
| Waterway dumping | Water pollution | High |
| Recycling | Reduced pollution | Low |
Used cooking oil that ends up in landfills or waterways creates long-term problems. Factories can lower emissions and reduce waste by recycling oil and using proper disposal methods.
Oil Purifiers and Environmental Sustainability
How Oil Purifiers Work
Oil purifiers use advanced filtration to clean cooking oil. These systems remove food particles, carbon, and other impurities from used cooking oil. Filtration happens through fine filters that trap unwanted materials, leaving the oil clear and ready for reuse.
Oil filtration systems operate in a continuous cycle. Workers pump used cooking oil through the filtration unit, which separates solids and contaminants. Clean oil returns to the fryer, while the system collects waste for proper disposal.
This process supports environmental sustainability by reducing the need for frequent oil changes. Factories use less new oil and create less waste. Cleaner oil also means less pollution when disposing of used cooking oil.
Extending Oil Life and Reducing Waste
Oil purifiers help food factories achieve longer oil life. Filtration removes impurities that cause oil to break down quickly during cooking. As a result, factories can use the same batch of oil for 25-50% longer than before.
This extension leads to significant operational cost savings. Many factories report a 30-40% reduction in oil expenses after installing oil filtration systems. Less frequent oil changes also mean less packaging waste and fewer deliveries.
Note: Longer oil life reduces the total amount of used cooking oil that needs disposal. This change lowers the environmental impact of food production and supports sustainability goals.
Improving Food Quality and Safety
Clean oil improves the quality and safety of cooked food. Filtration removes burnt particles and contaminants that can affect taste and appearance. Food cooked in purified oil looks better and tastes fresher.
Oil filtration systems also help maintain consistent cooking temperatures. Stable oil quality ensures that food cooks evenly and meets safety standards. This process supports better cooking oil management and reduces the risk of foodborne illness.
Sustainability improves when factories use less oil and produce less waste. Cleaner production methods protect the environment and support long-term business success. Food factories that invest in oil purifiers show a strong commitment to environmental sustainability.

Used Cooking Oil Recycling and Circular Economy
Filtration and Cleaning Steps
Used cooking oil recycling starts with cooking oil filtration. Workers collect used oil from fryers and other cooking equipment. Filtration systems remove food particles and impurities, making the oil cleaner for further processing.
After filtration, the oil goes through cleaning systems. These systems separate water and fine solids from the oil. Cleaned oil becomes ready for recycling or transformation into new products.
Tip: Regular maintenance of filtration systems improves the efficiency of used cooking oil recycling and reduces waste.
Recycling Oil into Biofuel
Recycling used cooking oil into biofuel supports a circular economy. Factories send filtered oil to recycling facilities. There, the oil undergoes chemical processes that convert it into biodiesel.
Waste oil recycling reduces the need for fossil fuels. Biodiesel made from recycled oil burns cleaner and produces fewer emissions. Many companies use this fuel in vehicles and machinery, supporting greener operations.
Waste oil recycling also keeps harmful substances out of landfills and waterways. This process protects the environment and helps factories meet sustainability goals.
Reducing Packaging Waste with Bulk Systems
Bulk oil delivery systems play a key role in oil recycling. These systems transport oil in large containers, reducing the need for single-use plastic and cardboard packaging. Factories receive fresh oil and return used oil in the same containers, creating a closed-loop system.
Bulk systems lower packaging waste and make oil recycling more efficient. Fewer deliveries and less packaging mean reduced environmental impact. Many food factories now use bulk systems to support waste oil recycling and improve sustainability.
Note: Switching to bulk oil delivery systems can help factories save money and reduce their carbon footprint.
Implementing Oil Purifiers in Food Factories
Steps for Adoption
Food factories can start by assessing their current cooking oil management systems. They should select oil purifiers that match their production needs and volume. Staff training on filtering cooking oil ensures proper use and maintenance, which leads to better oil management and lower costs.
A simple adoption process includes:
- Evaluate existing oil handling and waste procedures.
- Choose a suitable oil purifier for the factory’s size.
- Train staff on filtering cooking oil and oil management.
- Monitor oil quality and track costs over time.
Tip: Regular checks help factories measure the impact of new systems and adjust for higher profits.
Best Practices for Sustainability
Factories should follow best practices for filtering cooking oil to support sustainability. They can set up schedules for routine oil filtration and cleaning. Tracking oil usage and waste helps improve cooking oil management and reduce costs.
Using bulk oil delivery systems also cuts packaging waste. Factories that recycle used oil into biofuel show a strong commitment to sustainability. These steps help food factories lower costs and reduce their environmental impact.
Real-World Results
Many food factories report positive changes after installing oil purifiers. They see a 25-50% increase in oil life and a 30-40% drop in costs. Improved oil management leads to better food quality and less waste.
A table below shows the impact of filtering cooking oil:
| Benefit | Measurable Outcome |
|---|---|
| Oil life extension | 25-50% longer |
| Cost reduction | 30-40% lower costs |
| Food quality | Improved consistency |
| Environmental impact | Less waste generated |
Factories that focus on filtering cooking oil and strong oil management achieve higher profits and a smaller environmental impact.
Conclusion
Oil purifiers help food factories lower waste and protect the environment. These systems improve oil quality, reduce costs, and support responsible waste management.
- Explore oil purification and recycling solutions to boost sustainability.
- Review industry guides or contact experts for more information on starting this process.